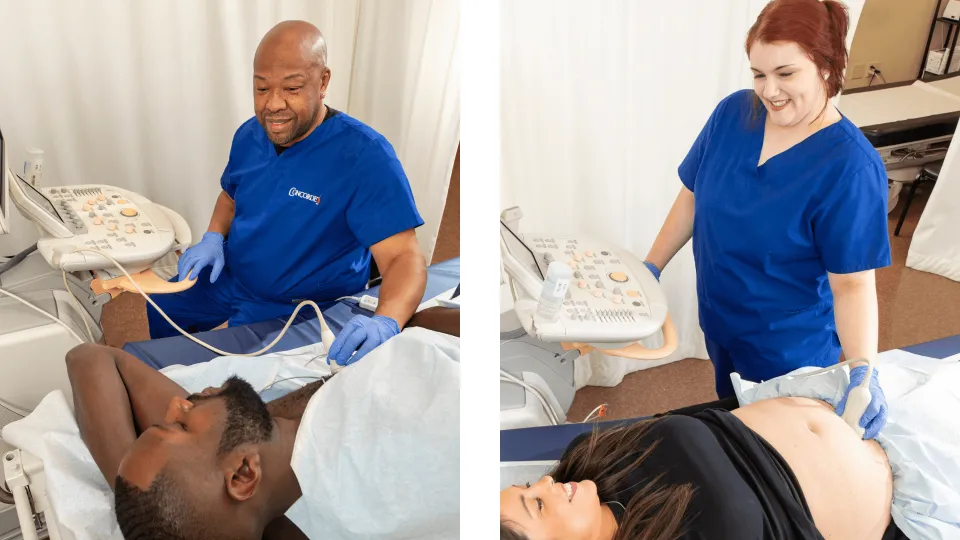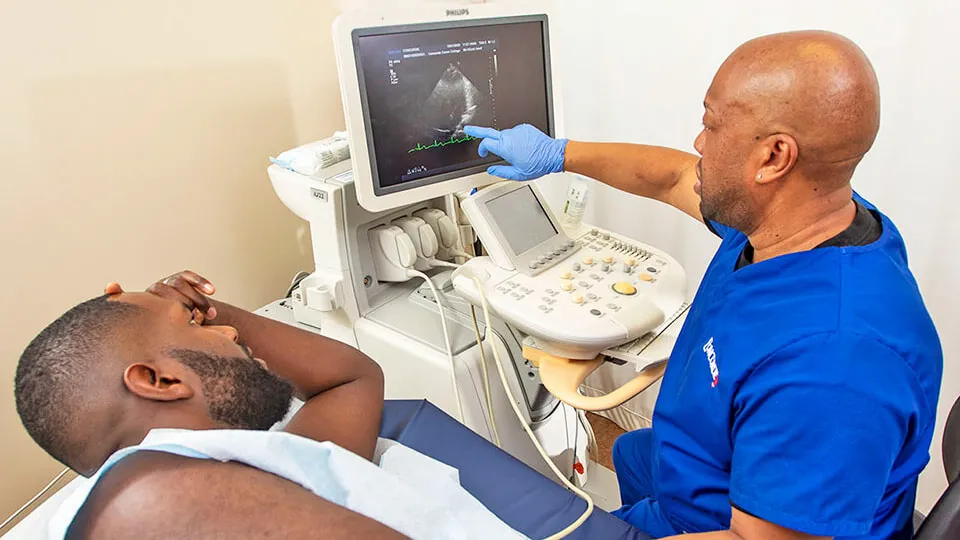
Cardiac sonographers, or echocardiographers, are health care professionals who use imaging technology to assist physicians in diagnosing heart conditions. They operate cardiac ultrasound equipment to create echocardiograms, which are dynamic images of the heart and its chambers, valves, and vessels. Echocardiograms provide cardiologists with vital insights into the condition of patients' hearts, enabling accurate diagnoses and effective treatment plans. Cardiac sonographers help physicians diagnose heart problems in patients of all ages, including children.
What Is Cardiac Sonography?

Cardiac sonography is a noninvasive diagnostic test that uses special equipment to direct high-frequency sound waves into areas of the patient's body. This diagnostic imaging technique uses ultrasound technology to create images of the heart and its components. These images help physicians diagnose various heart conditions, such as:
- Blood clots: Blood clots in the heart chamber can be life-threatening.
- Heart valve abnormalities: Aortic stenosis and mitral regurgitation are caused by malfunctions of one or more heart valves.
- Coronary artery disease: Narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries can cause heart attacks in patients.
- Cardiomyopathy: This heart muscle disease can cause the heart to thin, stiffen, thicken, or fill with abnormal substances, leading to potentially serious issues.
- Pericardial disease: Pericardial effusion is a fluid buildup around the heart, impacting heart function.
- Congenital heart defects: These structural abnormalities are present before or at birth and include coronary artery and septal defects.
- Aortic dissections and aneurysms: Abnormalities in the aorta can cause tears or weakened and bulging areas in the aortic wall, which can be life-threatening.
Unlike X-rays, which provide static images, medical sonography identifies abnormalities by real-time analysis of the heart's movement and function. The treatment uses ultrasound to create 2D and 3D images of body parts and organs, such as the breast, heart, and vascular system. Ultrasound technology is safe to use on pregnant patients, as it doesn't use radiation. Radiology uses X-rays, computed tomography scans, and magnetic resonance imaging to diagnose ailments such as broken bones, malformations, and cancer. Radiology can also evaluate pulmonary circulation, an important aspect of congenital heart defects.
Learn More About Concorde Career College's Cardiovascular Sonography Program
The Role of a Cardiac Sonographer
A cardiac sonographer assists physicians by preparing patients for procedures, preparing and maintaining diagnostic imaging equipment, operating the equipment to obtain diagnostic images, reviewing images for quality, recognizing normal and abnormal images, analyzing diagnostic information, and recording findings. Cardiac sonographers work to:
- Complete echocardiograms: Cardiac sonographers create detailed imaging of a patient's heart using ultrasound imaging.
- Evaluate heart conditions: During an echocardiogram, a diagnostic cardiac sonographer analyzes the blood flow and examines the heart's walls, chambers, and valves to assess the patient's overall heart health.
- Assist physicians: Cardiac sonographers assist physicians in advising patients about treatment options.
- Record data: Cardiac sonographers record test results and patient data from echocardiograms.
- Prepare patients: Before a procedure, the cardiac sonographer discusses the process and addresses the patient's questions and concerns.
- Prepare exam rooms: Cardiac sonographers maintain sonography equipment and prepare examination rooms for procedures.
- Position patients: The cardiac sonographer positions the patient for optimal imaging during an echocardiogram procedure.
- Review images: Cardiac sonographers review images for quality to ensure they have the necessary information for diagnosis.
- Analyze results: Cardiac sonographers analyze the image results to check for diagnostic information or abnormalities in the heart and its components.
- Communicate results: Cardiac sonographers share echocardiogram results with physicians, other health care professionals, and patients.
Cardiac sonographers may also help schedule appointments and clean equipment, depending on the job requirements and setting.
Related: What Are the Different Types of Sonographers? | How To Become an Echocardiogram Technician
Education and Training Requirements
Diagnostic Medical Sonography Program at Concorde
Diagnostic medical sonographers typically need formal education, such as an associate's degree or a postsecondary certificate. Aspiring cardiac sonographers should complete the following steps:
- Graduate from high school. Cardiac sonography programs require a high school diploma. While in high school, candidates should focus on science courses and skills, specifically human anatomy and biology, to prepare for a higher course of study.
- Earn a college degree. Students can earn an associate or bachelor's degree in a field related to cardiac sonography. Coursework in these programs includes classroom and lab work and hands-on training. Concorde's Cardiac Sonography Program offers an associate degree on campuses at various locations. Students can complete the program in as few as 20 months.
- Pass a certification exam. After completing their training program, candidates must gain certification. The American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography, National Board of Echocardiography, and Cardiovascular Credentialing International offer credentials for cardiac sonographers.
Acquire relevant licensing. Candidates should check with the state they plan to work in to determine if it requires licensure. Licensing is available to health care professionals who have completed their degree and certification in cardiac sonography.
Career Outlook and Opportunities
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects overall employment of cardiovascular technologists and medical sonographers to grow 11% between 2023 and 2033. This growth rate is much higher than the average for other occupations. An estimated 9,400 positions should open each year over the next decade due to transfers within the workforce and retirement. The need to diagnose cardiac conditions in older patients will increase as the baby boomer generation ages.
Advancements in Cardiac Sonography Technology
Cardiac sonographers have seen several advancements in the technology they use.
3D and 4D Imaging Capabilities
One of cardiac sonography's most significant innovations is 3D echo imaging software that allows physicians to manipulate images by slicing them on any plane. Slices are 3D images that specialists can rotate to look at from every angle. 4D technology can reconstruct data into 3D images repeatedly in milliseconds[6]. Other advancements in 4D technology include:
- Color flow in real time
- Multidimensional imaging
- Multiple axis views of the heart
Portable Ultrasound Devices
Previously, patients would need to attend a radiology suite or similar at a health care facility for cardiac sonography procedures. With advancements, the medical technology offers more compact equipment. Portable ultrasound devices allow physicians to diagnose patients anywhere, including in their homes, reducing stress and anxiety and traveling to and from appointments.
Artificial Intelligence in Image Analysis
Cardiac sonography is using AI to assist in image analysis and diagnosis. AI can help improve patient care by creating a consistent and reliable process that is easy and quick for health care providers. Institutions are using AI to process and diagnose cardiovascular scans by detecting heart disease and improving radiology images.
Related: New and Emerging Trends in Cardiac Sonography and Diagnostic Imaging
Challenges and Future of Cardiac Sonography
The future of cardiac sonography is promising, particularly with advancements in AI. This technology can enhance diagnostic accuracy and streamline workflow, allowing cardiac sonographers to focus more on patient care.
This evolution also brings challenges. The integration of ultrasound across various medical fields complicates the use and settings of sonography machines. This complexity necessitates ongoing training and adaptability. Sonographers must stay current with the technology and its applications. Balancing technological advancements with clinical practice is essential to the continued success of cardiac sonography in improving patient outcomes.
Related: Cardiovascular Tests for Nurses and Sonographers to Know
Train to Become a Cardiac Sonographer
Cardiac sonographers play a vital role in diagnosing heart conditions. Their work involves performing echocardiograms, which provide crucial insights into various heart issues. Cardiac sonographers prepare patients, operate imaging equipment, analyze results, and communicate findings to physicians.
Candidates typically require an associate degree and certification to enter this field. The demand for cardiac sonographers is projected to grow, driven by an aging population and technological advancements, including 3D and 4D imaging and portable devices. AI is also emerging to enhance diagnostic accuracy, although it presents challenges related to increased complexity in machine settings. The field offers rewarding career opportunities while requiring ongoing training in new technologies and techniques.
Related: 10 Reasons To Train for a Career in Cardiovascular Sonography
https://www.wsong.org/blog/when-is-ultrasound-better-than-an-x-ray
https://www.bls.gov/ooh/healthcare/diagnostic-medical-sonographers.htm
https://www.indeed.com/hire/job-description/diagnostic-medical-sonographer
https://www.concorde.edu/diagnostic-programs/diagnostic-medical-sonography/jacksonville
https://www.gehealthcare.com/insights/article/current-issues-and-opportunities-in-sonography
https://www.bls.gov/ooh/healthcare/diagnostic-medical-sonographers.htm#tab-6
Take The Next Step Towards a Brighter Future
Interested in learning more about our Cardiovascular Sonography program?
We have a Concorde representative ready to talk about what matters most to you. Get answers about start dates, curriculum, financial aid, scholarships and more!