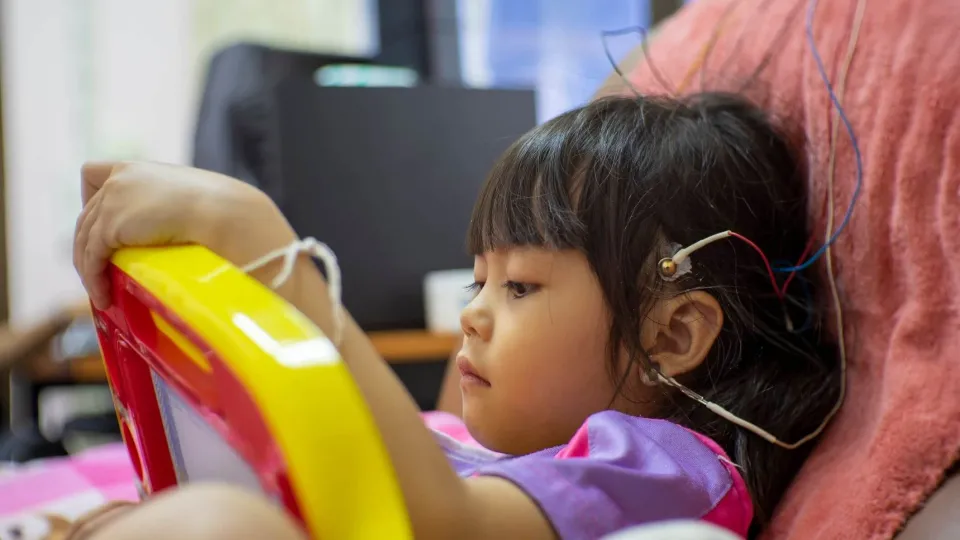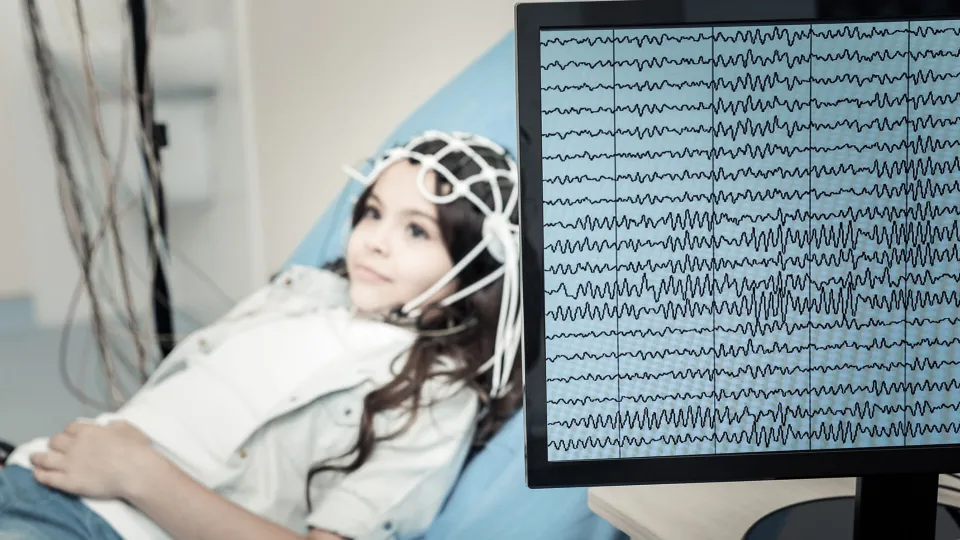
An electroencephalogram, or EEG, technician has a fundamental role in diagnosing and treating neurological disorders by conducting tests that record electrical activity in the brain. Working with neurologists, these health care professionals help identify conditions such as epilepsy, sleep disorders, and brain injuries.
EEG technicians work in hospitals, clinics, and specialized diagnostic centers. Their expertise in operating EEG equipment is essential for ensuring accurate and reliable test results, making this career path fulfilling and impactful. These tests can involve routine EEGs, sleep EEGs performed while the patient sleeps, ambulatory EEGs that involve a portable device that records over a prolonged period, video EEGs performed in hospital over several days, or prolonged EEGs which take over an hour to complete. This article explores the role of an EEG technician to help students decide whether this is the right career path for them.
Educational Requirements

To prepare for a career as an EEG technician, high school students should focus on specific coursework that builds a strong foundation in relevant subjects, such as the following.
Mathematics
Taking three years of mathematics in high school can help develop analytical thinking. Consider courses in algebra, geometry, and possibly statistics. These courses can help build the foundation needed for understanding data and calculations in EEG technology.
Science
Three years of science can help students understand the body's systems and electrical activity. Focus on biology, physics, and chemistry in high school. This can provide an understanding of human anatomy and the physiological processes related to brain function.
English
Strong communication skills are essential. EEG technicians often work with neurologists, nurses, and other health care professionals and interact directly with patients. Taking an English course will help students communicate effectively.
Social Sciences
Courses in social sciences can provide insights into patient care and the health care environment. This can improve a student's interpersonal skills and problem-solving abilities. Social sciences can improve a student's verbal and nonverbal communication abilities, which are important for explaining procedures to patients who may be anxious about an EEG. Understanding psychology and sociology can also help technicians understand diverse patient backgrounds and behaviors.
Related: A Day in the Life of a Neurodiagnostic Technologist
Post-Secondary Education Options
There are several educational paths to becoming an EEG technician, ranging from certificate programs to associate degree programs and bachelor's degrees.
Associate Degree Programs
Many students opt for associate degree programs like the one offered by Concorde Career College, which typically take up to two years to complete. These degrees cover subjects such as neuroanatomy, EEG instrumentation, and patient care. Students may apply for certification after they complete these programs.
Certificate Programs
Candidates may complete certificate programs in about 12 months. These programs provide essential training in EEG techniques and patient care. Students learn how to perform EEGs and monitor brain activity while gaining theoretical knowledge and hands-on skills.
Bachelor's Degree Programs
A bachelor's degree takes four years to complete. Some universities, such as the University of North Carolina at Charlotte, offer bachelor's degrees that include advanced topics and training in neurodiagnostic technology.
Accredited Programs
An accredited EEG program ensures the education provided meets industry standards and prepares students for certification. Programs accredited by the Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs are especially respected in the field.
Concorde Career College offers the Neurodiagnostic Technology Program, which students can complete in as little as 17 months. It's a CAAHEP-accredited program and provides students with the opportunity to acquire the essential foundations to work as an EEG technician, including electrode placement, brain and nervous system testing, and measuring brain responses.
Clinical Training and Internships
Most programs include clinical rotations, which often last several months, where students gain hands-on experience with EEG procedures under the supervision of experienced technicians.
During this period, students apply their theoretical knowledge in a real-world setting. They will learn how to operate and place EEG equipment, prepare patients for the exam, and accurately record data. While internships are not always required, they offer valuable practical experience. By gaining useful skills, such as data interpretation and patient communication, students are better equipped to enter the workforce.
Certification and Licensure
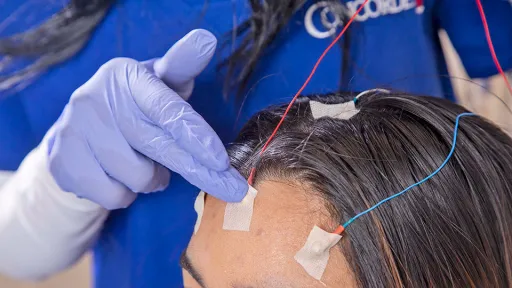
Related: How To Become a Neurodiagnostic Technologist
Certification and licensure options include the following.
National Certification
Candidates may apply for certification to become a professional EEG technician. The most widely recognized is the Registered Electroencephalographic Technologist credential, offered by the American Board of Registration of Electroencephalographic and Evoked Potential Technologists. To qualify for certification, candidates need to:
- Complete an NDT CAAHEP-accredited program or have equivalent clinical experience.
- Document a specified number of EEG procedures — usually 50.
- Hold a high school diploma or equivalent.
- Hold a valid CPR or BLS certification.
The R. EEG T. examination is a computer-based test that costs $700 and includes multiple-choice questions covering theoretical and practical aspects of EEG technology, such as equipment and patient care. Candidates have four hours to complete the test. Certification is valid for five years, at which time the technician needs to renew the certification through continuing education credits in neurodiagnostic or related areas and pay a recertification fee.
State Licensure
Licensure requirements for EEG technicians vary by state. EEG technicians don't require state licensure in most areas, as certification through organizations such as ABRET is sufficient. Some states are considering laws that may require EEG technicians to have a license before practicing, while Louisiana and New Jersey already require a license for technicians performing polysomnography studies. Candidates should check local regulations and state laws in their area for the latest guidelines.
Skills and Qualities
To pursue a career as an EEG technician, the following key skills and qualities are essential:
- Technical expertise and knowledge of EEG equipment
- Attention to detail
- Compassion and empathy
- Communication
- Interpersonal skills
- Problem solving
- Patient care
- Troubleshooting
- Data analysis
- Time management
- Computer literacy
- Analytical skills
Career Outlook and Advancement

Related: 5 Types of EEG Tests for Brain Wave Monitoring
There are plenty of options for career advancement as an EEG technician, with opportunities for specialization in areas such as intraoperative monitoring or neurodiagnostic technology. Technicians may also choose leadership positions, such as lead technologist or clinical supervisor roles.
Take the Next Step
Becoming an EEG technician offers rewarding and stable employment in health care, with growing demand and various opportunities for advancement. With the increasing need for neurological testing, skilled EEG technicians are more essential than ever. If you're passionate about health care and technology, this career could be ideal for you. Ready to start your journey in health care? Get started by contacting our admissions team at Concorde today.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some FAQs with answers.
How long does it take to become an EEG technician?
It usually takes one to two years to complete an EEG technician program, depending on whether students pursue a certificate or an associate degree. A bachelor's degree will take a minimum of four years.
Do I need a license to work as an EEG technician?
License requirements vary by state. Some states require licenses, while others don't. Applicants should check local regulations to discover their state's conditions.
What certification do I need to become an EEG technician?
The most recognized certification is the R. EEG T. credential from ABRET. To qualify, candidates must complete an accredited program, gain clinical experience, and pass the examination.
What skills are important for EEG technicians?
Key skills include technical proficiency with EEG equipment, attention to detail, communication skills, problem-solving abilities, interpersonal skills, and patient care.
Can I specialize as an EEG technician?
EEG technicians can specialize in areas such as evoked potential testing, sleep studies, or intraoperative monitoring, which can lead to career advancement and higher salaries.
Where do EEG techs work?
EEG technicians work in hospitals, clinics, and specialized diagnostic centers, such as epilepsy treatment centers or sleep study programs.
What are the pros and cons of being an EEG Technician?
The role of an EEG technician can be rewarding and have positive career growth and advancement opportunities. However, the job is physically demanding, high-pressured, and may involve long hours or irregular work schedules, including late nights, weekends, and public holidays.
Neurodiagnostic Technology. (2024). Concorde Career Colleges. https://www.concorde.edu/diagnostic-programs/neurodiagnostic-technology
How to Become an Electroencephalographic (EEG) Technician. (2024, December 11). Healthcaredegree.com. https://www.healthcaredegree.com/lab/eeg-tech
Neurodiagnostic Tech Certification & Licensure Guide – Trusted Health. (2024). Trustedhealth.com. https://www.trustedhealth.com/allied-career-guide/neurodiagnostic-tech/certification-guide
Admissions. (2025). Concorde Career Colleges. https://www.concorde.edu/admissions
Take The Next Step Towards a Brighter Future
Interested in learning more about our Neurodiagnostic Technology program?
We have a Concorde representative ready to talk about what matters most to you. Get answers about start dates, curriculum, financial aid, scholarships and more!