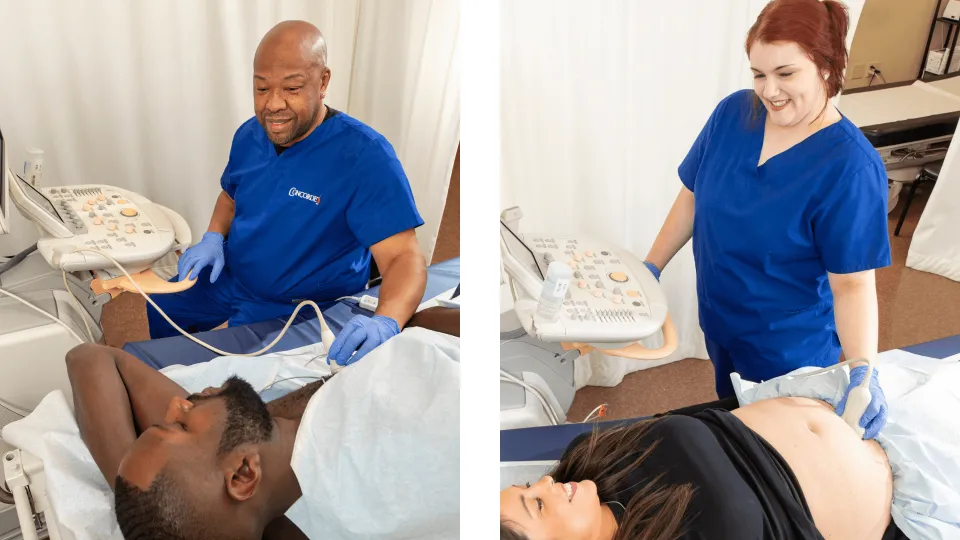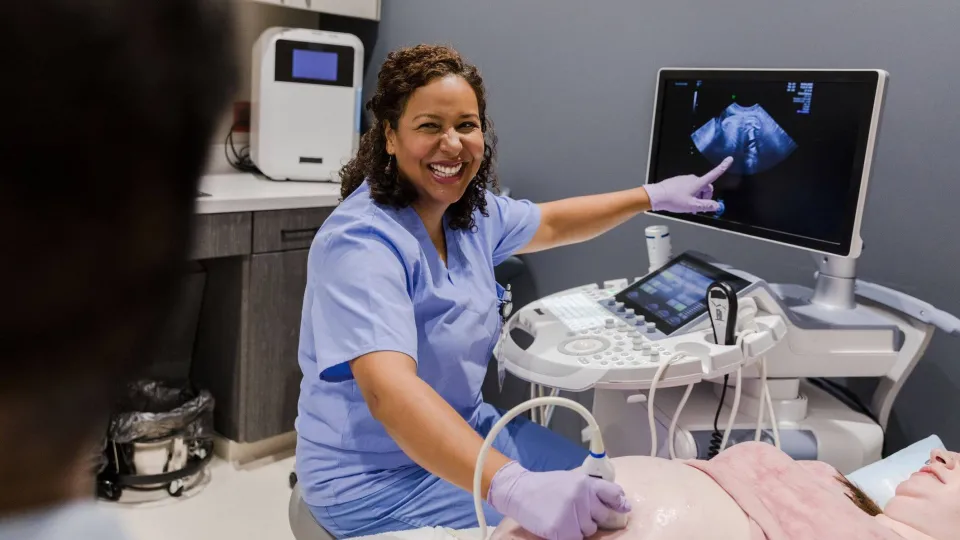
Using high-frequency sound waves to create diagnostic images of the body, ultrasound technology is a key aspect of health care. This non-invasive imaging method helps detect and monitor conditions such as high-risk pregnancies, cancer, and heart defects, making it an essential tool in medical diagnostics. With the field projected to grow by 11% with approximately 9,400 new job openings for diagnostic medical sonographers and cardiovascular technologists and technicians in the next decade, there's increasing interest in careers within this space.
However, the terms ultrasound technician and sonographer can be confusing for potential students looking to explore these careers. Are they the same, or do they have distinct roles? This article will clarify the similarities and differences between these two professions to help students understand which role may be a more suitable match for their passions and career goals.
What Is an Ultrasound Technician?
An ultrasound technician is a health care professional who uses ultrasound technology to create diagnostic images of a patient's internal organs and tissues. This specialized equipment emits high-frequency sound waves, which bounce off the body to produce images known as sonograms. The goal of the images is to determine an accurate diagnosis of the patient's ailments.
Primary Responsibilities
The primary responsibilities of an ultrasound technician typically include the following:
- Preparing patients for their examinations by explaining the procedure and answering any questions or concerns.
- Programming and adjusting the ultrasound scanner to capture images from various angles and ensuring that the transducer is functioning correctly.
- Performing clinical assessments and diagnostic sonography examinations.
- Selecting and capturing still images that are necessary for diagnostic purposes.
- Assisting with the daily operations of the sonographic laboratory.
- Documenting images and preliminary observations for the physician to review.
In addition to these core duties, ultrasound technicians take care of the equipment, apply gel to improve the quality of the images, and communicate with patients throughout the process. Ultrasound technicians work in various health care settings, such as hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic imaging centers.
Related: How To Become a Diagnostic Medical Sonographer: Education and Certification
What Is a Sonographer?

A sonographer, also known as a diagnostic medical sonographer, is a specialized health care professional who also uses ultrasound technology for diagnostic imaging. However, unlike ultrasound technicians, sonographers focus more on interpreting the results. They provide important information that assists medical professionals in diagnosing and monitoring medical conditions.
Primary Responsibilities
The primary responsibilities of a sonographer include the following:
- Specializing in specific areas such as obstetrics, cardiac sonography, or vascular sonography to focus on specific populations or medical conditions.
- Analyzing the captured images to detect any abnormalities, assisting physicians in diagnosing conditions.
- Supporting radiologists or physicians during invasive procedures, such as vascular ultrasound procedures and ultrasound-guided biopsies.
- Completing necessary documentation and maintaining accurate medical records for each patient, including recording diagnostic data.
Related: Guide to a Career in Sonography: Here's What To Know
Key Similarities
Are an ultrasound technician and a sonographer the same thing? The answer is both yes and no. A career as an ultrasound tech or sonographer has many similarities, which may include the following:
- Using ultrasound machines to produce images for diagnosis.
- Working in hospitals and clinics.
- Interacting directly with patients.
- Having similar educational training in diagnostic medical sonography or a related field.
- Contributing to the diagnostic process by providing essential imaging services.
- Having similar certification, such as from the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography.
What's the Difference Between Sonographer and Ultrasound Technician Roles?
There are a few substantial differences between an ultrasound tech and a sonographer, which may include the following:
| Aspect | Ultrasound Technician | Sonographer |
| Job Focus | Primarily operates equipment | Assumes a broader role, including analysis |
| Level of Analysis | Basic image capture | In-depth image interpretation |
| Specialization | General imaging | Specific areas (e.g., cardiac, obstetrics) |
| Certification Requirements | Requires basic certification | Requires specialized credentials |
| Career Advancement | Limited to technical roles | More opportunities for specialization, supervision, and leadership |
Education and Training
To pursue a career as a sonographer or ultrasound technician, students must meet the following educational requirements:
- Minimum education: Students must have an associate degree in diagnostic medical sonography or a related field.
- Accreditation: Education programs should be accredited by the Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs to ensure that certain minimum professional standards are met.
- Bachelor's degree: Some institutions offer bachelor's degree programs that provide advanced training opportunities.
- Certificates: For students with prior health care degrees, certificate programs may be available as a pathway into sonography.
- Coursework: Programs should cover common courses such as anatomy, physiology, medical terminology, applied sciences, and ultrasound technology.
It usually takes two to four years to complete all the required education for an ultrasound tech or sonographer, depending on the degree level. For those looking to pursue career advancement on their own schedule, Concorde Career College offers an associate degree program that provides entry-level general sonographers with the opportunity to gain the knowledge, skills, and behavior needed to pursue a career in this field. For those who wish to specialize in cardiovascular sonography, there is also a Cardiovascular Sonography Program. Each course can be completed in as little as 20 months.
Related: 6 New and Emerging Trends in Cardiac Sonography and Diagnostic Imaging
Certification and Licensing
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, professional certification in medical sonography is not mandatory to work in the field. However, many employers expect or prefer it, so a candidate's potential job prospects may increase with certification. Once technicians receive certification, they will need to meet specific requirements to maintain their status. Common certifications include the following:
ARDMS
Employers often prefer candidates with professional certification from recognized bodies such as the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography. These certifications include the following options:
- Registered Diagnostic Medical Sonographer.
- Registered Diagnostic Cardiac Sonographer.
- Registered Vascular Technologist.
Other certifying bodies for a sonographer or ultrasonographic technician include the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists and Cardiovascular Credentialing International.
State Licensing Requirements
Some states require licenses for both ultrasound technicians and sonographers. Currently, only four states in the U.S. require medical sonographers to be licensed. These states include:
- New Hampshire
- New Mexico
- North Dakota
- Oregon
In these states, sonographers must meet specific requirements to obtain and maintain their licenses. This typically involves completing an accredited sonography program and passing relevant certification exams. Sonographers and ultrasound technicians are also required to renew their licenses annually or every two years, depending on the relevant license or certification.
Continuing Education Requirements
Continuing education ensures that ultrasound technicians and sonographers maintain their certifications and stay updated with advancements in an ever-changing field. These requirements differ according to the certification but typically involve completing 24 to 36 continuing education credits every two to three years. For ARDMS certification, technicians should aim to complete 30 continuing education credits every three years. Technicians or sonographers can earn credits by attending workshops, completing online courses, or taking part in relevant industry conferences.
Career Outlook
The job outlook for both ultrasound technicians and sonographers is promising. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the national demand is projected to rise by 11% from 2023 to 2033, much faster than the average for any other occupation. This demand is largely due to the nation's aging population, which relies more and more on diagnostic imaging services. Approximately 15,200 new positions are projected each year as demand rises from current workers changing careers, leaving the workforce, or retiring.
Take the Next Step
While both ultrasound technicians and sonographers are important for diagnostic imaging in health care, their roles are slightly different. Students should consider their personal interests, desired responsibilities, and career goals when choosing between an ultrasound technician and sonographer path. Both roles offer promising career prospects and job security within a rapidly growing health care field. Prioritize accredited programs and certification requirements to stand out when pursuing a career in this area. Visit Concorde Career College and get started on training for an ultrasound or cardiovascular technician or sonography career by contacting an admissions representative.
Diagnostic Medical Sonographers and Cardiovascular Technologists and Technicians, Including Vascular Technologists : Occupational Outlook Handbook: : U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. (2019, April 12). Bls.gov; U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. https://www.bls.gov/ooh/healthcare/diagnostic-medical-sonographers.htm
Oroville. (n.d.). Www.orovillehospital.com. https://www.orovillehospital.com/media/file/Ultrasound%20Technician%20Job%20Description.pdf
Diagnostic Medical Sonography. (2023). Concorde Career Colleges. https://www.concorde.edu/diagnostic-programs/diagnostic-medical-sonography
Cardiovascular Sonography | Concorde Career Colleges. (n.d.). Www.concorde.edu. https://www.concorde.edu/diagnostic-programs/cardiovascular-sonography
Diagnostic Medical Sonographers and Cardiovascular Technologists and Technicians, Including Vascular Technologists : Occupational Outlook Handbook: : U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. (2019, April 12). Bls.gov; U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. https://www.bls.gov/ooh/healthcare/diagnostic-medical-sonographers.htm 1 & 5
ARDMS Registry Renewal Fees. (n.d.). ARDMS. https://www.ardms.org/maintain-certification/registry-renewal/
Admissions. (2025). Concorde Career Colleges. https://www.concorde.edu/admissions
Take The Next Step Towards a Brighter Future
Interested in learning more about our Diagnostic Medical Sonography program?
We have a Concorde representative ready to talk about what matters most to you. Get answers about start dates, curriculum, financial aid, scholarships and more!