Radiologic technologists are important in health care, as they operate equipment that captures detailed scans of the human body. These images help physicians diagnose and treat a wide range of medical conditions. As technology in medical imaging grows, radiologic technologists must continually improve their technical skills to stay effective.
The profession is growing, with employment projected to increase by nearly 5% from 2024 to 2034, which is faster than the average for most professions, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. This article covers the top 10 technical skills that can help radiologic technologists succeed in their careers.
What Is a Radiologic Technologist?
A radiologic technologist, also called a rad tech, is a health care professional who scans the human body using equipment to help diagnose and treat conditions. Key responsibilities include:
- Preparing patients for scans, including explaining the procedure
- Using X-ray machines, CT scanners, MRI machines, or mammography equipment to take clear scans
- Positioning patients for accurate results
- Following safety rules to reduce radiation exposure
- Monitoring patients during scans for comfort and safety
- Keeping records and sharing images with doctors
- Helping doctors to review the scans
- Cleaning and maintaining the equipment
Radiologic technologists typically require an associate degree in radiologic technology and must pass a certification exam, such as the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists exam, to become licensed. Concorde Career College offers its Radiologic Technology Associate Degree program that can be completed in as little as 20 months at Concorde - Aurora and Concorde - Memphis. Some professionals pursue additional certifications in specialized areas such as MRI or mammography. Rad techs work in hospitals, imaging centers, outpatient clinics, and doctor's offices. They work closely with radiologists, physicians, and other health care professionals to guarantee the most reliable diagnoses.
Operating Imaging Equipment
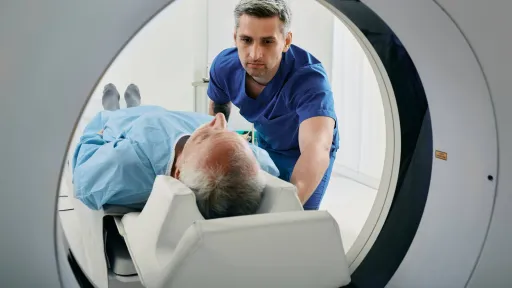
Being competent in using various imaging modalities or scanning machines is one of the most essential skills for radiologic technologists. These include:
- Taking X-rays or scans to help diagnose injuries or illnesses
- Using computed tomography scanners to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body
- Using magnetic resonance imaging scanners to scan soft tissues such as muscles and organs
- Using fluoroscopy to provide live, moving images
- Using an ultrasound to check a fetus during pregnancy or mammography to detect breast cancer
Mastering these technical skills for radiologic technicians ensures the images are accurate and reduces the need for repeat scans. This is important for minimizing a patient's exposure to radiation.
Patient Positioning
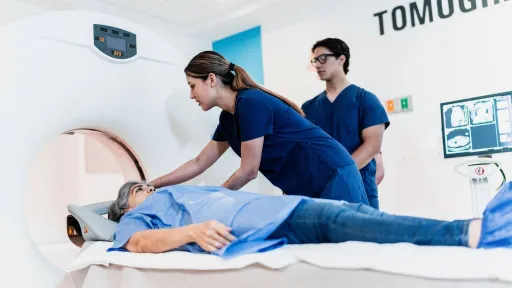
Positioning the patient correctly is one of the top radiography skills for getting high-quality images. A radiologic technologist must understand human anatomy and position the patient's body for the scan. This skill helps limit the patient's exposure to radiation and guarantees the most accurate results. A radiologic technologist must also follow safety guidelines, such as using shields and keeping radiation doses as low as possible.
Image Production and Evaluation
Radiologic technologists must check the scans for quality before they submit them to the doctor for review. Quality checks include:
- Making sure the image is clear and has the right contrast
- Looking for anything that could interfere with the diagnosis, such as artifacts
- Adjusting the exposure if the image is too dark or too bright
These quality checks help ensure the scans are as clear as possible. This reduces the need for repeat scans.
Radiation Safety and Protection
Radiologic technologists follow safety guidelines to protect patients, coworkers, and themselves from radiation exposure. This includes using the following techniques:
- As low as reasonably achievable principle: ALARA ensures radiologic technologists focus on limiting radiation exposure to patients, themselves, and others by taking all reasonable precautions without compromising the quality of the scan.
- Lead shielding: Shielding involves using lead aprons, gloves, or thyroid shields during imaging procedures.
- Collimation: This process narrows the X-ray beam to focus only on the area of interest.
Rad techs also monitor radiation levels with dosimeters and follow safety standards set by the ARRT and the International Atomic Energy Agency.
Computer and Digital Imaging Skills
Radiologic technologists need to understand anatomy and common medical conditions. Understanding the structure of the body helps them capture clear, accurate images of specific areas and make quick decisions during imaging.
Knowing the difference between normal and abnormal scans means rad techs can do preliminary assessments and communicate well with radiologists. Identifying issues before a radiologist reviews the scans helps speed up diagnosis and treatment.
Medical Terminology and Anatomy Knowledge
Radiologic technologists follow ethical guidelines and protect patient confidentiality. They follow Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 regulations, protect patient information, and obtain consent before the scan. They may need to explain the procedure to the patient, make sure they understand why it's important, and answer their questions. Professionalism and integrity are key. Radiologic technologists should be respectful and compassionate when dealing with patients. They should create a safe, comfortable environment and communicate clearly with patients and consulting doctors.
Quality Control and Equipment Maintenance

Radiologic technologists need to be confident in spotting and resolving technical issues with imaging equipment. This includes picking up any malfunctions as soon as possible. They may also perform regular maintenance checks and support biomedical engineers when repairs are needed.
Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving
Radiologic technologists have strong communication skills because they work directly with patients, doctors, and health care teams. They understand how to explain procedures clearly to ease anxiety, work with radiologists and referring physicians, and provide detailed reports when necessary. Good communication helps improve patient care and teamwork.
Attention to Detail
The field of radiologic technology, with the advent of digital imaging, artificial intelligence, and 3D imaging, is always evolving. Radiologic technologists should stay updated on:
- AI-driven imaging analysis tools
- Digital radiography enhancements
- New contrast agents and imaging techniques
Related: Helpful Traits of a RAD Tech
Adaptability and Continuous Learning
Lifelong learning is key. Many states require ongoing education to maintain a license. Professional development can include:
- Attending industry conferences
- Pursuing specialized certifications (e.g., MRI, CT, mammography)
- Taking part in mentorship programs and peer collaboration
Related: ARRT Certification, A Comprehensive Guide
Building a Successful Career
Mastering these technical skills prepares radiologic technologists for success. From technical proficiency in imaging equipment to patient care and continuing education, these competencies improve job performance and result in high-quality scans. As medical technology advances, radiologic technologists who develop their skills and can adapt to changing times will thrive in this profession.
If you're considering a career as a radiologic technologist, Concorde offers a Radiologic Techology training program, as well as programs in Diagnostic Medical Sonography and Cardiovascular Songography at select campuses, each of which can be completed in just 20 months. Take the first step toward training in radiologic technology by contacting an admissions representative.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some questions people frequently ask about radiologic technologists:
What Are the Latest Advancements in Imaging Equipment for Radiologic Technologists?
The latest advancements include digital radiography with better image quality, 3D imaging capabilities such as tomosynthesis, AI-assisted image interpretation, dual-energy imaging, portable X-ray innovations, and advanced visualization techniques such as virtual reality and augmented reality.
How Does Patient Positioning Affect Image Quality in Radiologic Procedures?
Rad techs position the patient to align the relevant body part with the scanner. This reduces motion artifacts and distortions. Getting this wrong can result in blurry or unusable images.
What Are the Key Factors in Evaluating the Technical Quality of Medical Images?
Technologists assess the quality of the scans based on spatial resolution, contrast resolution, noise characteristics, and artifacts.
What Are Common Quality Control Procedures for Radiologic Equipment?
Common quality control procedures include acceptance testing, assessing images, dosimetry, assessing patient dose, and measuring radiation.
How Does Attention to Detail Impact Patient Safety in Radiologic Procedures?
Attention to detail ensures radiologic technologists create high-quality images. This makes it easier to diagnose a condition. Rad techs need to position and align specific body parts, tube angles, and the image receptor correctly, which requires precision.
What Are the Emerging Technologies in Radiologic Technology That Professionals Should Be Aware Of?
AI is changing the future of radiology, with AI algorithms helping with image analysis and interpretation. This has the potential to improve the accuracy and speed of diagnoses.
What Are the Most Common Types of Imaging Procedures Performed by Radiologic Technologists?
Radiologic technologists perform many common imaging procedures, such as X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, ultrasounds, and bone densitometry scans.
How Often Do Radiologic Technologists Need To Update Their Skills and Knowledge?
Rad techs need to complete continuing education every two years and renew their certification and registration every year.
U.S. BUREAU OF LABOR STATISTICS. (2024, April 12). Radiologic and MRI Technologists : Occupational Outlook Handbook: : U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Bls.gov. https://www.bls.gov/ooh/healthcare/radiologic-technologists.htm
Take The Next Step Towards a Brighter Future
Interested in learning more about our Radiologic Technology program?
We have a Concorde representative ready to talk about what matters most to you. Get answers about start dates, curriculum, financial aid, scholarships and more!